Many will be surprised that Peter Kraljic published the article “Purchasing must become Supply Management” in the 80s (1983) and the supply positioning matrix is still in force to classify, identify and determine strategies in purchasing management: Kraljic .
The concept is quite basic, but very powerful. It consists of classifying the purchasing categories, facing the impact (on the y- axis of the Cartesian plane) and the complexity (on the x- axis of the Cartesian plane). As a result, there is a classification into four quadrants: routine (low impact, low complexity), leveraged (high impact, low complexity), bottlenecks (low impact, high complexity) and strategic (high impact, high complexity).
The most interesting thing is that each quadrant has extensive documentation on strategies to put into practice, such as reverse auctions for the leveraged, price agreements for routines, supplier development for bottlenecks, win-win relationships with strategic ones, for example. mention a few.
The objective of this text is to give some practical advice to build a Kraljic matrix for companies and generate a palpable and real deliverable as input to establish a clear route in this exciting world of strategic supply management.
How to construct a Kraljic matrix?
Excel is recommended as a tool and to see graphically the type is XY (dispersion) with the Bubble subtype . In this type, 3 dimensions are needed: X Values of the series, the Complexity Data column , Y Values of the series, the Impact Data and Bubble Size column of the series, the Relevant Values Data column (explained later).
Each criterion must be composed of subcriteria that will be rated with a value between 2,4,6,8 or 10 (even Likert scale) where 2 will represent a lower impact or complexity and 10 will represent a greater impact or complexity and will have a weight ( %) within each group (Complexity or Impact) that allows weighting.
An important recommendation is to carry out the exercise separately for categories of goods and for categories of services , given their nature. Additionally, for the qualification of each criterion it is suggested to carry out exercises similar to the probability voting of a risk matrix, where various actors involved give the qualification and after that, it is checked that there is fairness of the opinions and in case of divergences They can argue in a socialization.
(In this link you can download a template that we have prepared to put the methodology into practice)
As an example, the data visualization would look like this:
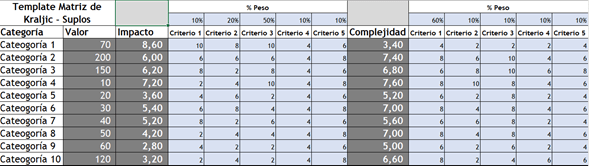
And the graph associated with this categorization would be something like what is shown in the following graph:

What criteria should be considered to construct the Kraljic matrix?
Some of the suggested criteria to consider in the construction of the matrix are the following:
Impact
- Number of Lines: number of requests or requisitions that arise in a given period of time.
- Criticality for the process: possibility of stopping a process or project in the event of not having the supply or provision of the service.
- Urgency: periodicity with which an unplanned urgent need arises.
- Previous period amount : historical purchase value.
- Budgeted amount for next period: budgeted purchase value for the category.
Complexity
- Number of Suppliers: corresponds to the number of recurring suppliers in this category, the greater the number of suppliers, the less complexity.
- Location where the good or service is delivered: in the event that the process or project that requires the good or service is located in areas with some logistical complexity.
- Substitute or homologous products: determine if there is the possibility of replacing the good or service with another type of solution.
- Logistics and transportation: identify all types of complexities in logistics, such as import, means of transportation, among others.
- Delivery Time (Lead Time): at this point it is important to compare the history if the delivery times adjust to the needs and the orders are placed sufficiently in advance to allow deliveries to be met.
- Availability of the Good or Service in the market: verify the seasonality or shortage that may occur.
- Technical Specifications of the Good or Service: in case of manufacturing that involves inspections and quality assurance.
Relevant values: Amount of the budgeted purchase for the category under review.
This same methodology can be applied to various aspects of supply management, such as to suppliers of a certain category, to the buyers themselves in their management or even as a prioritization tool for invoice payments in case of cash difficulties at a certain time. , the exercise is reduced to selecting criteria that represent each of the axes and having an objective qualification that allows designing a strategy.




